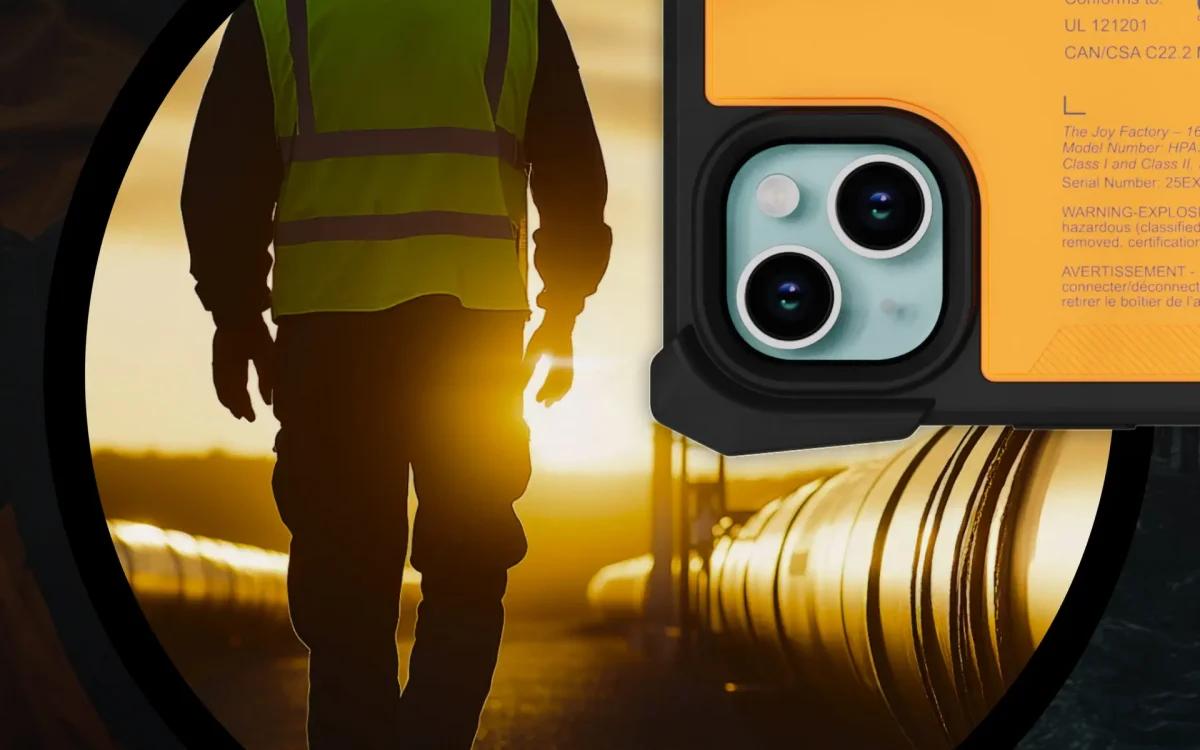
Class I Division 2 iPhone Solution
Accessories That Add Value:
- Mounts for forklifts, walls, and rolling carts that secure devices in place.
- Certified chargers that eliminate electrical discharge risk.
- Carrying solutions like shoulder straps or belt clips for hands-free access.
Tangible Benefits for Connected Workers:
- Field workers can carry, mount, and use devices without needing to remove gloves or break protocol.
- Reduces risk of damage from drops, spills, and vibrations.
- Enhances uptime by preventing device failure mid-shift.
Ask vendors to provide documentation that confirms certifications are current and applicable to your zone type.
Step 3: Define Safe Usage Protocols and Train Teams
Objective: Align frontline behavior with safety standards to protect personnel and equipment.
Even with certified hardware, safety depends on user behavior. You must document procedures and train employees before deploying devices into the field.
Best Practices:
- Prohibit charging inside hazardous zones unless using certified equipment.
- Set inspection intervals to verify case seals and device condition.
- Create clear steps for what to do if a device shows signs of damage.
Training Focus Areas:
- Safe handling and carry methods.
- How to spot equipment wear or malfunction.
- Device cleaning and maintenance procedures.
Include mobile device training in onboarding and conduct annual refreshers to maintain compliance.
Step 4: Configure iPhones with Secure, Field-Ready Software
Objective: Enable productive workflows and control how devices are used in the field.
Once the physical setup is safe, the focus shifts to digital readiness. Devices should be locked down, standardized, and connected to backend systems.
Key Tools to Deploy:
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) to enforce policy, push updates, and track usage.
- Augmentir for digital workflows, guided tasks, and frontline enablement.
- RedZone for lean operations, real-time metrics, and digital Kaizen.
Configuration Tips:
- Remove access to app stores and personal apps.
- Enable remote wipe for lost or stolen devices.
- Use geofencing to restrict use in ultra-hazardous areas.
A well-configured iPhone becomes more than a phone. It becomes a certified, mobile workstation that fits in a pocket.
Step 5: Build a Maintenance and Audit Program
Objective: Maintain compliance and performance over time through structured review processes.
Certification is only valid if the conditions remain unchanged. You need an ongoing inspection and audit process to keep devices safe and compliant.
Key Activities:
- Inspect case integrity monthly, including seals and wear points.
- Maintain digital logs for each device, including usage and service history.
- Schedule third-party audits annually for recertification.
Use Asset Management Tools:
- QR codes to track devices and link to service logs.
- Alerts for inspection due dates or overdue maintenance.
- Role-based access for audit teams to review compliance status.
Benefits of this Approach:
- Reduces surprise device failures in the field.
- Workers know who to contact if they spot an issue.
- Management has full visibility into device readiness and compliance.
A proactive maintenance strategy prevents small issues from becoming safety incidents or operational disruptions.
Who Benefits from Deploying iPhones in Hazardous Locations?
| User | Direct Benefits |
|---|---|
| Field Technicians | Hands-free operation, real-time issue reporting, faster repairs |
| Maintenance Engineers | Digital inspection forms, remote troubleshooting, step-by-step guides |
| Safety Managers | Instant incident logging, audit-ready data, live alerts |
| Quality Inspectors | Photo capture for defects, checklist validation, GPS tagging |
| Operations Leaders | Live performance dashboards, better asset visibility, reduced downtime |
Each role benefits from faster communication, better visibility, and tools that simplify complex tasks. With the right deployment, iPhones become productivity multipliers without compromising safety.
Final Takeaway: Technology Only Works…When It Works
Deploying iPhones in hazardous locations is a practical step toward modern, connected operations. But without the right planning and certified accessories, it introduces unnecessary risk.
The aXtion Extreme for iPhone 15 enables safe, certified deployment into Class I Division 2 environments. It gives teams the tools they need to work efficiently while meeting all relevant safety and compliance standards.
Next Steps
If you’re planning a deployment or upgrading an existing system, connect with us to:
- Review certification requirements for your facility.
- Get a tailored quote for aXtion Extreme kits and accessories.
- Learn how to integrate iPhones into your digital workflow strategy.
Deploy Safe, Certified Solutions today!
For companies operating in oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, utilities, or other high-risk sectors, deploying mobile technology like iPhones in hazardous environments is not just a tech upgrade. It’s a business-critical initiative that improves safety, productivity, and real-time decision-making.
However, success depends on more than just handing out devices. It requires certified equipment, process alignment, and operational discipline. This guide walks through a practical deployment framework and shows how certified solutions like the aXtion Extreme for iPhone 15 create real-world value for field teams.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand Hazardous Location Classifications: Identify and understand the specific classifications relevant to your deployment [1].
- Select Certified iPhone Cases and Accessories: Choose protective cases and accessories that meet industry standards [2].
- Implement Safety Protocols and Training: Establish robust safety protocols and provide comprehensive training to employees [3].
- Configure and Secure iPhones: Utilize industry-specific software and implement security measures to ensure safe and efficient operation [4].
- Monitor and Maintain Compliance: Conduct regular inspections and compliance audits to maintain high safety standards [5].
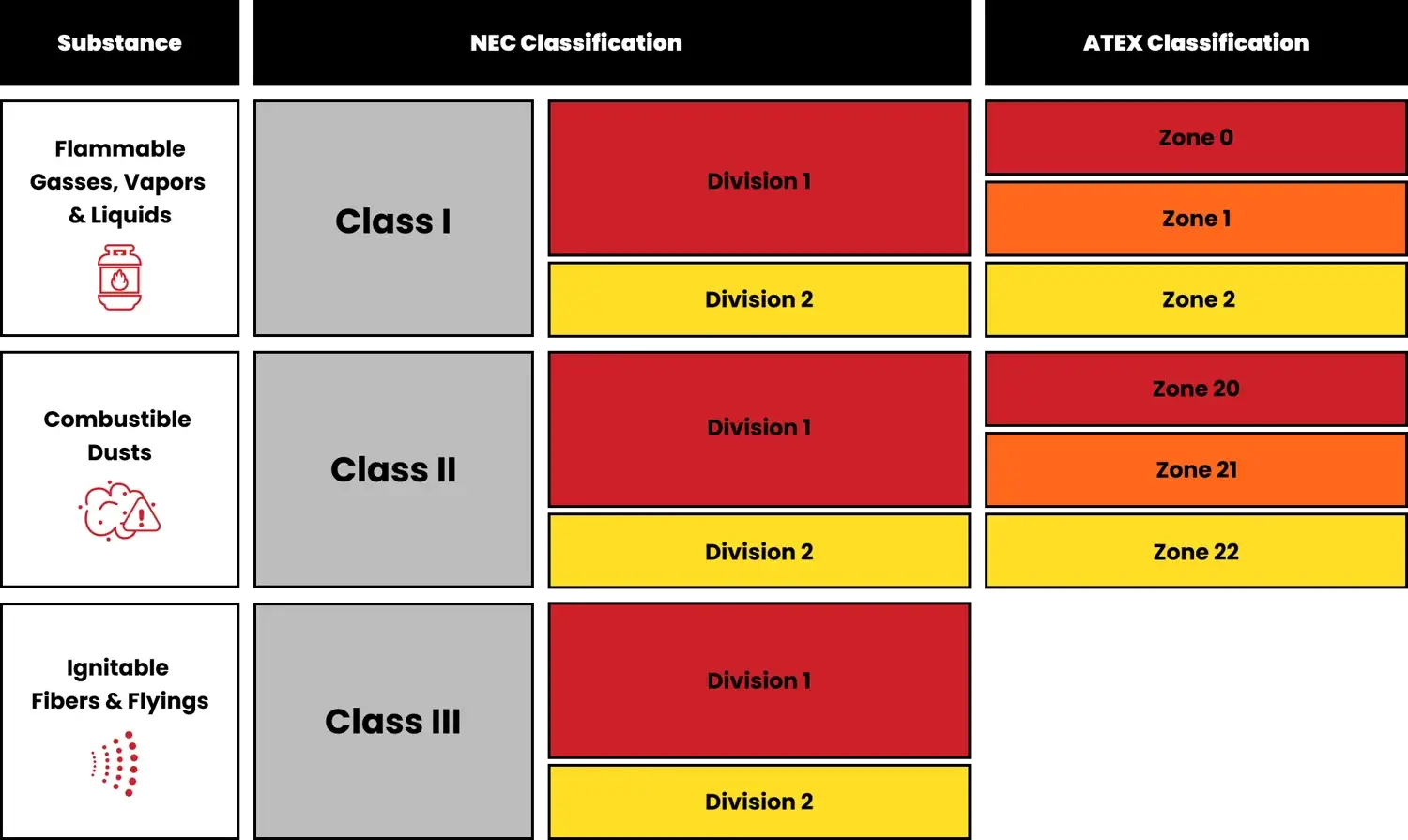
Step 1: Confirm Your Hazardous Area Classification
Objective: Ensure the iPhone deployment matches safety regulations for your specific operating environment.
Start by identifying the correct classification of your work zone. This determines the types of devices and accessories allowed by law.
Common Standards:
- ATEX (EU) for explosive atmospheres in European facilities [6].
- IECEx (International) for globally recognized certification across regions [7].
- NEC (U.S.) with Class, Division, and Group-based definitions [8].
Common Use Case:
- Class I, Division 2 or Zone 2 areas where flammable gases or vapors may be present under abnormal conditions [9].
Why?
- Reduced risk of compliance violations or shutdowns.
- Fewer injuries caused by incorrect equipment use.
- Faster safety audits and insurance approvals.
Consult a qualified safety engineer to validate the classification. This step ensures you are selecting the right certified technology.
Step 2: Equip iPhones with Certified, Hazardous Location Certified Solutions
Objective: Ensure device safety by using certified, rugged enclosures that prevent ignition.
An iPhone alone is not safe for use in explosive environments. It needs to be housed in a case that eliminates ignition risk, protects from environmental exposure, and withstands rough handling.
Why Choose the aXtion Extreme for iPhone 15:
- Class I Division 2 certified.
- Built for high-impact environments with full drop and vibration protection.
- Features sealed ports, spark-free materials, and integrated screen protection.
References
[1] Hazardous Location Classification Guide: NEC vs. IEC
[2] Hazardous Environment Classifications: NEC vs. IEC
[3] Comparison of IEC & NEC Area Classifications – Inst Tools
[4] Top Benefits of Waterproof & Rugged Smartphones in Harsh Environments
[5] The Science Behind Waterproof and Dustproof Phones – How Rugged Devices …
[6] Rugged Smartphones: The Ultimate Devices For Extreme Environments And …
[7] What are the differences between NFPA 70 NEC, ATEX and IEC Ex Rated …
[8] Classes and Divisions Compared to ATEX/IECEx Zones
[9] Guide to Hazardous Location Standards: NFPA 70 NEC, ATEX, IECEx







